Engine knock sensor: What is its function?
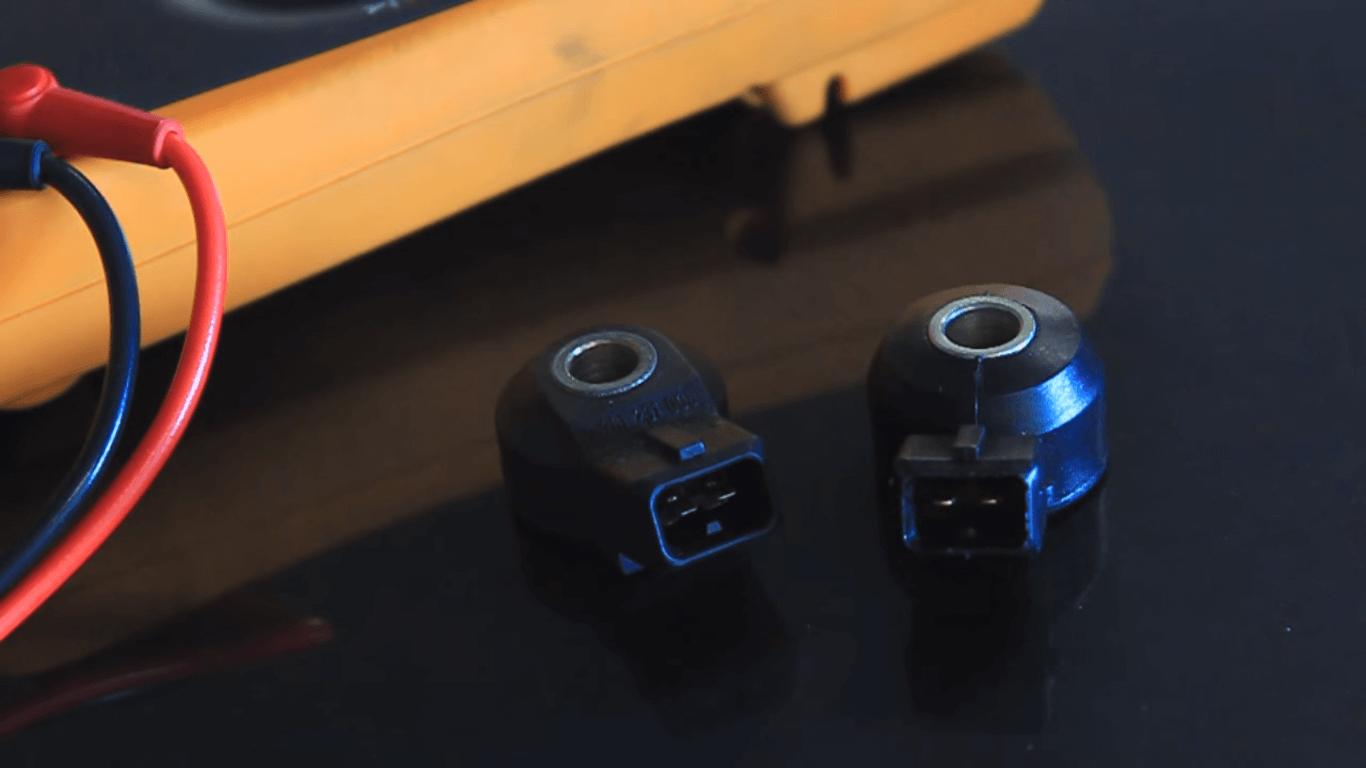

The engine knock sensor is a piezoceramic sensor in the spark-ignition engine block. The purpose of this sensor is to measure engine noise during its operation (combustion).
The knock sensor records the occurrence of engine knocking, characterized by an increase in pressure and engine noise (knock), from which the name of this phenomenon is derived.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
What is detonation combustion?
Engine knocking is a negative phenomenon during combustion in spark-ignition engines, which is acoustically manifested by a knocking sound. Why does it occur, though? It's caused by an improper fuel mixture burning at the wrong moment.
When the mixture of fuel and air enters the cylinder, it is heated through compression. Then when the mixture is supposed to ignite, its temperature is at the limit of spontaneous combustion. At this moment, the mixture is ignited by the spark of the spark plug.
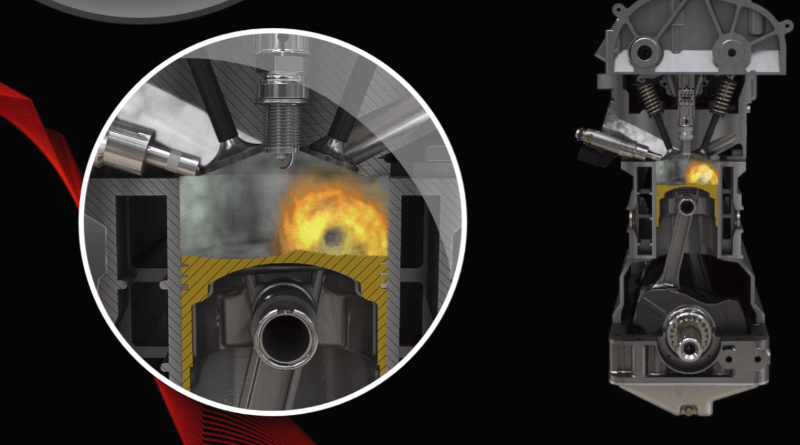
Engine Detonation: What is it, and how to prevent it?
However, if the mixture ignites by itself, without the help of a spark plug spark, its burnout is inhomogeneous and, therefore, of poor quality. In this case, shock waves begin to spread in the cylinder space, reflected from the internal walls of the combustion chamber, and are acoustically manifested by the already mentioned knocking sound.

Spark plugs: How do they work, and what's their lifespan?
How does the engine knock sensor work?
Thus, the engine knock sensor is used to detect engine knocking, which can (with prolonged exposure) cause damage to the engine. The knock sensor is connected to the engine control unit, which adjusts the ignition advance in the event of detecting knocking, thereby preventing it.

Engine Control Unit: What is its function?
An engine with a knock sensor can burn fuel with a lower octane number than it is designed for. Such an engine can permanently adjust its ignition advance for fuel with a lower octane number, which will, however, decrease its performance. At the same time, though, the engine is equipped with a knock sensor and can take advantage of high-octane fuels.
By using several knock sensors (one for each cylinder), it is possible to achieve selective regulation of the ignition of each cylinder, according to the working conditions in which the given cylinder is currently located.

Engine Power And Torque: Which of these parameters is more important?
The knock sensor helps the engine achieve efficient mixture combustion by reducing the ignition advance, bringing it closer to the detonation combustion threshold. In this way, the engine's performance is optimized, but fuel consumption and exhaust gas emissions are also reduced.
This sensor also protects engine components that participate in the combustion process (cylinder head, pistons, piston rings, valves, cylinders, cylinder liners, cylinder head gasket, and so on).
A malfunction of the engine knock sensor most often causes the following:
Engine noise (engine knocking)
Engine overheating
Increased fuel consumption