Engine Designations: TDI, MPi, TSI, HTP, do you know them all?

In the automotive world, we come across countless abbreviations, including engine designations. The manufacturer determines these engine designations, but who is to know the number of different letters and their combinations?
For this reason, we have decided to prepare this comprehensive list for you, in which we will shed light on common engine designations and their meaning.
Indholdsfortegnelse
CDi
CDi (Common-rail diesel injection) refers to diesel engines with direct fuel injection. These engines are equipped with a Common-rail system (a common fuel pipe for all cylinders). Mercedes and Chrysler use CDi engines.
CDTi
CDTi (Common-rail diesel turbo injection) refers to turbocharged diesel engines with direct fuel injection. They are equipped with the Common-rail system (a common fuel pipe for all cylinders) and are used by the Opel brand.
CRD
CRD (Common rail diesel) refers to diesel engines with direct fuel injection. Engines with this designation are used by the American automobile manufacturers Chrysler, Dodge, and Jeep.
CRDi
CRDi (Common rail diesel injection) refers to diesel engines with direct fuel injection. The only difference from CRD is that this designation is used by Korean car companies such as Hyundai or Kia and Japanese Mitsubishi.
CVVT
CVVT (Continuously variable valve timing) refers to engines with continuously variable valve timing, thanks to which they achieve higher performance and lower consumption. Kia, Hyundai, and Volvo use this designation.
DCi
DCi (Diesel Common-rail injection) refers to diesel engines with Common-rail technology, i.e., direct fuel injection and a common fuel pipe. Renault and Nissan use this designation.
DDiS
DDiS (Direct Diesel injection System) refers to a turbocharged diesel engine with a Suzuki common rail system.
Common Rail: How does it work, and what are its advantages?
DiDT
DiDT (Direct injection Turbo Diesel) refers to a turbocharged diesel engine with a common rail system.
DTI
DTI (Direct Turbo Injection) stands for turbocharged diesel engine with direct injection.
FSI
FSI (Fuel Stratified Injection) refers to the gasoline engine with a direct fuel injection of the VW concern.
GDi
GDi (Gasoline direct injection) refers to petrol engines with direct gasoline injection. This designation is used by car companies Mitsubishi, Kia, and Hyundai.
Engines with direct fuel injection can burn fuel much more efficiently. Thus, they are more powerful, and their consumption is lower.
HDI
HDI (High-pressure direct injection) refers to an engine with high-pressure direct injection. These engines can be equipped with the OverBoost function (it increases the power for a short time after pressing the pedal).
HDi engines are equipped with a turbocharger and produced by the PSA Group using Common Rail technology. They are specific for their well-developed gait.
HTP
HTP (High torque performance) also refers to an engine with high torque. Three-cylinder engines of Škoda, Seat, and Volkswagen brands are denoted by the abbreviation HTP.
The engine was created by removing one cylinder from a 1.6 16V 77kW engine and began production in 2002. However, this engine has become the target of ridicule over the years and earned many nicknames.
i-VTEC
i-VTEC technology is the highest level of development of Honda's variable valve timing and lift. It is actually a classic VTEC combined with VTC (Variable Timing Control) technology. VTC is a mechanism that allows you to change the position (rotation) of the camshaft smoothly.
Honda only uses this system on the intake camshaft. VTC is active all the time at all speeds. With the i-VTEC system, turning the camshaft by up to 50 degrees is possible.
JTD
JTD (Jet Turbo Diesel) refers to a common rail turbocharged diesel engine used by Fiat, Alfa Romeo, and Lancia. The first generation of common-rail diesel engines from Fiat under the designation JTD was also known under the initials "uniJet" Turbo Diesel.
JTDM
JTDM, in other words, Jet Turbo Diesel Modified (Multijet), is a designation for engines with Common-rail technology and, thus, direct fuel injection. Fiat was the first to come up with this system in 1997 for Alfa Romeo engines, followed by Mercedes-Benz. Multijet is widely used by Fiat, Alfa Romeo, and Lancia, but also by Chrysler, Jeep, and Maserati.
MIVEC
MIVEC (Mitsubishi Innovative Valve timing Electronic Control system) is a designation for the Mitsubishi car company's engines, equipped with a variable valve timing and valve lift system.

MIVEC: Variable valve timing and valve lift
This valve control system is used to improve the engine's volumetric efficiency, thereby increasing engine power and reducing fuel consumption and the number of emissions produced.
MZ-CD
MZ-CD - (Mazda – Common rail Diesel) refers to Mazda turbocharged diesel engine with a Common rail system.
MPi
The MPi abbreviation indicates engines equipped with multi-point fuel injection (Multi Point Injection). In this type of injection, fuel is injected in front of the intake valve using injection valves assigned to individual cylinders.
This means that one injection valve is assigned to each cylinder, which delivers the required fuel for that cylinder.
SDI
SDI (Suction diesel injection) refers to diesel engines with atmospheric filling and direct fuel injection produced by Volkswagen Group. Since these engines are not turbocharged, they provide less power compared to turbocharged engines of the same displacement.
SDI engines were produced as in-line four-cylinder or five-cylinder engines. Because they are structurally simpler than turbocharged engines, they are also more reliable while consumption remains unchanged.
SPi
The SPi abbreviation indicates engines equipped with single-point fuel injection. The single-point injection is a type of indirect fuel injection in which fuel is injected through a single injection valve into a common intake manifold chamber upstream of the throttle valve.
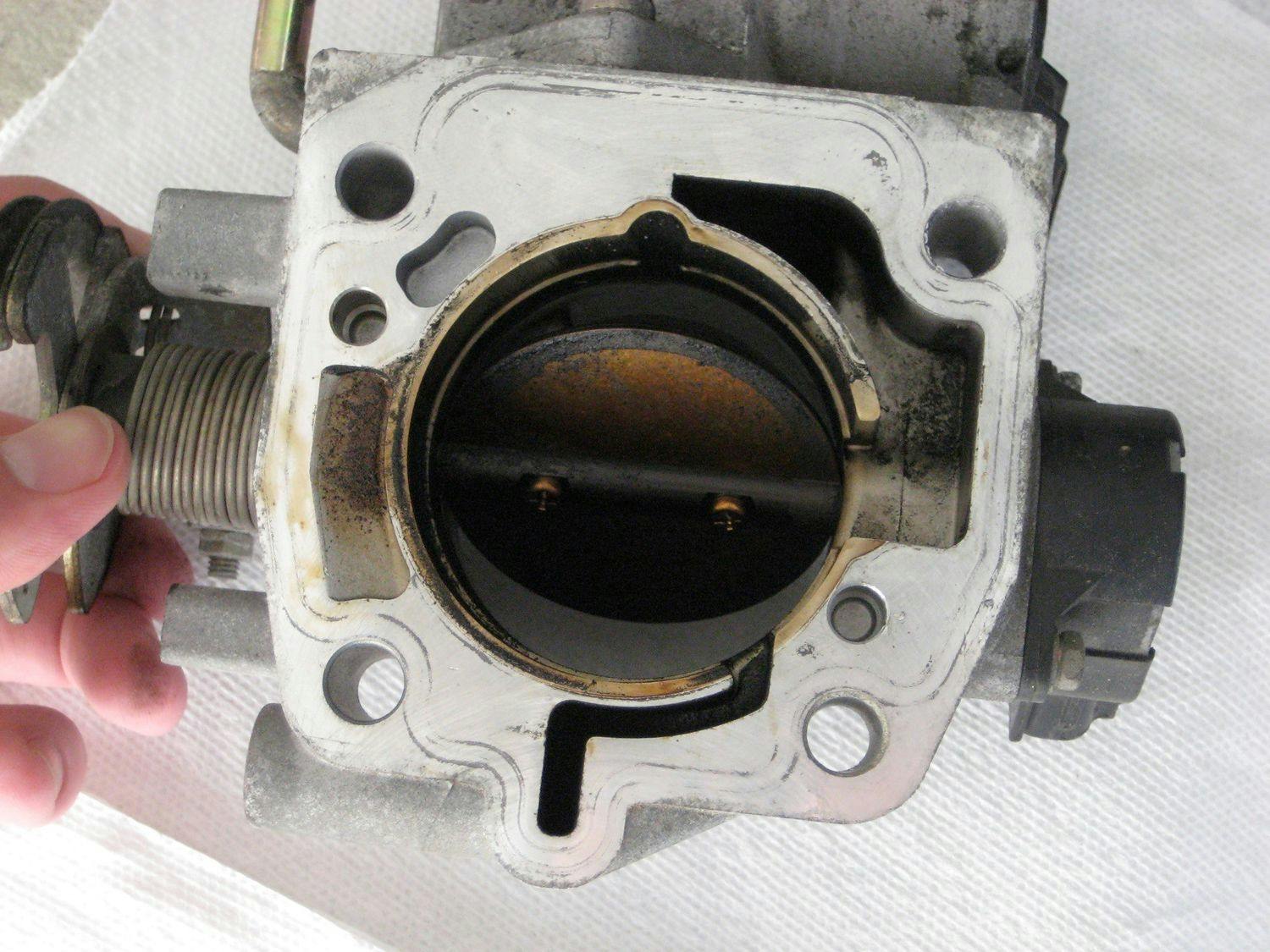

Throttle valve: How it works and its possible malfunctions
After the fuel is injected into the intake manifold chamber, it mixes with the flowing air and passes through the throttle valve. Behind the throttle, the intake pipe is divided into separate chambers, with the help of which the mixture of fuel and air is led to the individual cylinders of the engine.
TDI
TDI (Turbocharged direct injection) refers to supercharged diesel engines with direct injection produced by Volkswagen Group. In many countries, the abbreviation TDI is registered as a trademark of the Volkswagen Group, and these engines are widespread primarily in Europe.
TDI-PD
TDI-PD - (TDI – Pumpe Düse) denotes a turbocharged direct injection diesel engine with a pump-nozzle unit.
TDDi
TDDi (Turbo diesel direct injection) refers to diesel engines with direct fuel injection. The Ford brand uses this designation. The newer generation of diesel engines (TDCi) has a more refined and less noisy operation compared to TDDi.
TDCi
TDCi (Turbo diesel common-rail injection) refers to diesel engines with direct fuel injection with the Common-rail system. These engines are the newer generation of TDDi engines used by Ford.
TCe
TCe (Turbo Control efficiency) is the designation of a gasoline engine supercharged by a turbocharger. It was first introduced in 2007 in the Renault Twingo GT model. To make them easier to identify, the automaker uses a number indicating the size of the given engine's volume and the horsepower value (e.g., 1.2 TCe 115 Energy - such an engine has 115 horsepower).

Horsepower: What is it, and why is it important?
T-GDi
T-GDi (Turbo gasoline direct injection) refers to petrol engines with direct gasoline injection additionally equipped with a turbocharger. This designation is used by car companies Hyundai and Kia.
TGI
TGI (Turbo Gas Injection) refers to Volkswagen cars equipped with turbocharged engines with direct natural gas injection (CNG).
These engines are structurally derived from TSI engines, specifically from the 1.4 TSI engine. TGI engines can burn gasoline and compressed natural gas, i.e., CNG.
TSI
TSI (Turbocharged Stratified Injection) refers to turbocharged gasoline engines with direct fuel injection produced by the Volkswagen Group. TSI engines are equipped with a single-scroll turbocharger and are characterized by a very high performance from a small volume.
The first generation of these engines had problems with the timing chains, but over time this problem was solved by replacing the chain and tensioner.
TFSI
TFSI (Turbo Fuel Stratified Injection) refers to the turbocharged gasoline engine with a direct fuel injection of the VW Group. Compared to the TSI engine, which is equipped with a single-scroll turbocharger, the TFSI engine uses a twin-scroll turbocharger.
TwinAir
TwinAir refers to a two-cylinder petrol engine built by Fiat Powertrain Technologies (FPT). At the same time, it was equipped with an electro-hydraulic system that could open the intake valve independently of the position of the camshaft.
The ability to independently open the valve significantly improves the quality and accuracy of filling the engine. In 2011, this engine was awarded engine of the year with the awards "Best engine under 1.0 liter", "Best new engine," "Best ecological engine," and "International engine of the year."
Twin Spark
Alfa Romeo uses Twin Spark technology. Twin in translation means double, and Spark is a candle, that is, a double candle. Twin Spark, abbreviated as TS, thus means double ignition through two spark plugs for each cylinder.
The advantage of double ignition is the achievement of more optimal combustion and, therefore, higher performance and lower emissions.
Valvematic
Valvematic is a technology of the Toyota car company that allows the lift of the intake valves to be continuously changed. Toyota uses this technology in its cars, equipped with gasoline (petrol) units.
Valvetronic
Valvetronic is a designation for BMW engines equipped with variable valve lifts. It is, therefore, a variable valve lift system, which, in combination with variable valve timing, allows you to change the position of the camshaft independently of the position of the crankshaft and can also change the lift and length of time during which the valve is open.
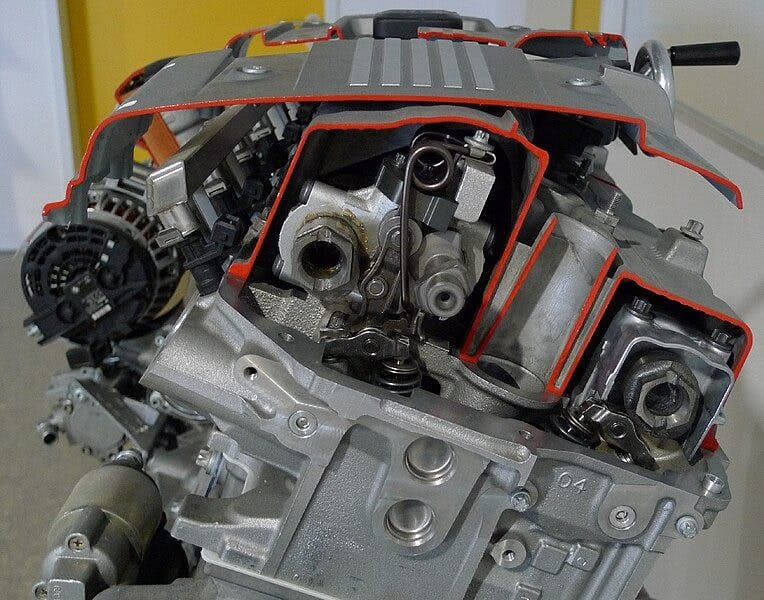

Valvetronic: How does the variable valve lift system work?
This technology is used to optimize engine parameters. The Valvetronic system gives engines higher performance, lower fuel consumption, and lower emissions.
VTi
VTi (Variable valve lift and timing injection) refers to a petrol engine with variable valve timing, produced by the PSA Group (Peugeot, Citroen) and the BMW concern. This engine has two variants, namely 1.4 liters and 1.6 liters, used in Peugeot and Citroen cars.
VTEC
VTEC (Variable Valve Timing and Lift Electronic Control) refers to Honda engines equipped with variable valve timing and lift technology.
Variable valve timing technology is used to improve the engine's volumetric efficiency, thereby increasing engine performance and reducing fuel consumption and emissions.
Conclusion
After this article, we believe engine designations will no longer be a problem for you. However, if you did not find some engine designations in this list, do not hesitate to write us in the comments.