Multishaft engine: Did you know what type of engine it is?
A multi-shaft engine is a type of piston internal combustion engine equipped with multiple crankshafts. The multi-shaft construction enables the realization of single-piston, two-piston (engine with counter-rotating pistons), and multi-piston engines.
A multi-shaft engine is always equipped with more than one crankshaft. According to the number of shafts, this motor is more precisely called, for example, a two-shaft motor, a three-shaft motor, a four-shaft motor, and so on.
Table of Contents
Twin shaft motor
A twin-shaft engine may have two crankshafts located side by side with cylinders situated around them, or crankshafts situated on opposite sides of the cylinder, meaning one crankshaft on one side of the cylinder and a second crankshaft on the other side of the cylinder.
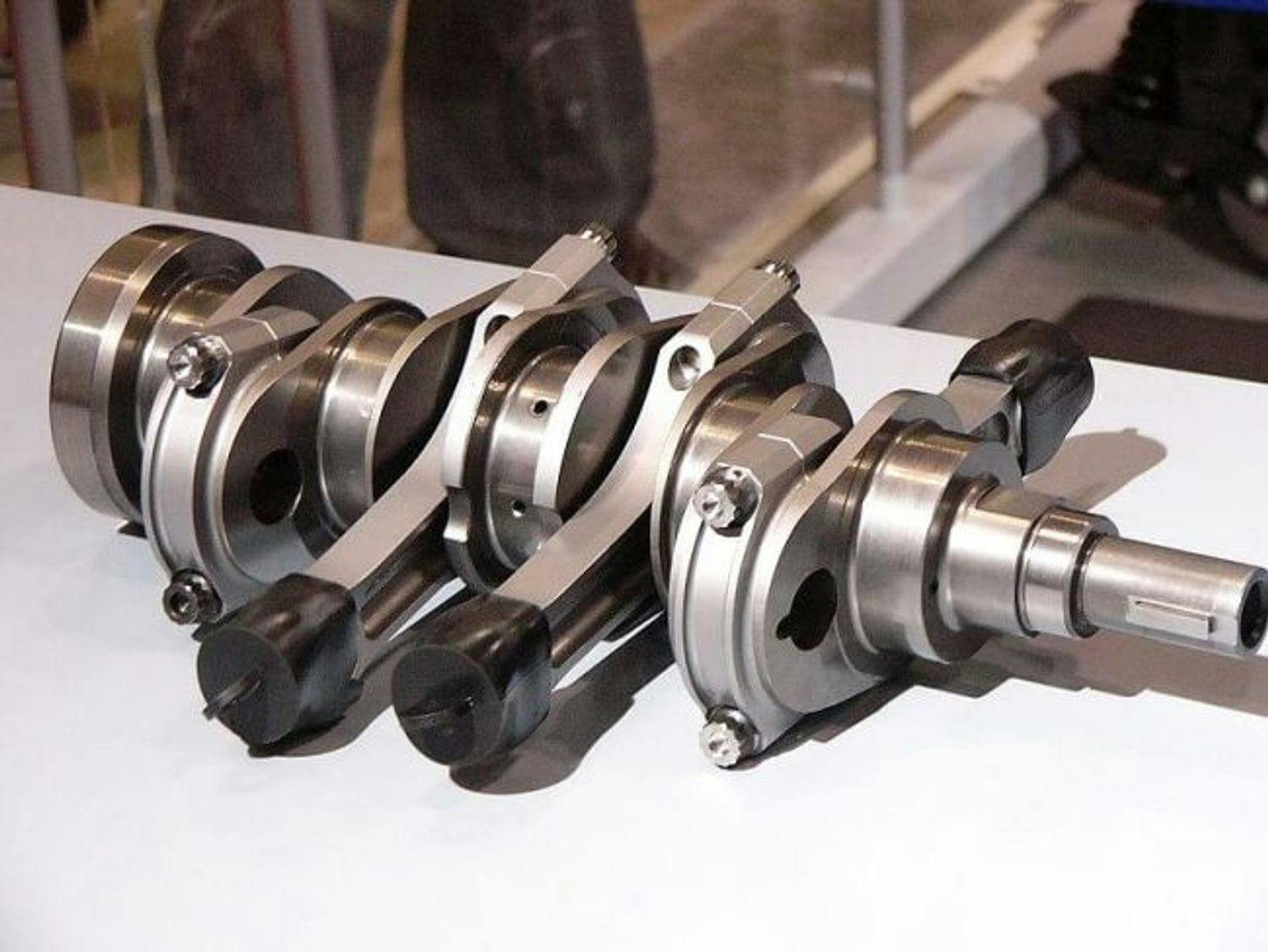

Crankshaft: What is it for, and what forces must it withstand?
If the crankshafts are located next to each other with the cylinders located around them, we distinguish the following engine designs:
U Engine
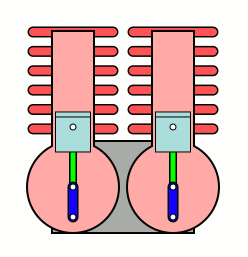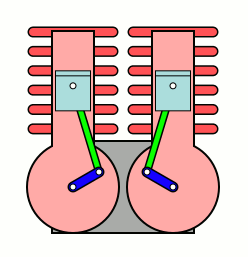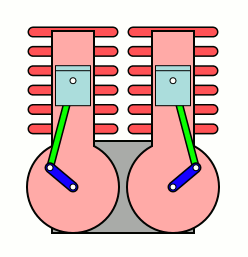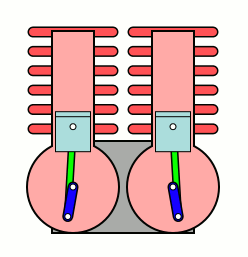
A U engine, also known as a parallel-cylinder engine, is a type of two-cylinder or two-row, two-shaft piston internal combustion engine. In this type of engine, the planes of the cylinder banks are parallel, and the two crankshafts are interconnected.
H Engine
The H engine is a four-cylinder or four-row, two-shaft piston internal combustion engine. With this type of engine, its cross-section forms the shape of the letter H, which is actually where its name is derived from.
Internal combustion engine: How does it work?
An H engine has two parallel crankshafts that are connected. If the crankshafts are located on opposite sides of the cylinder:
Engine with counter-rotating pistons (two-piston version)
A counter-rotating piston engine is a two-piston internal combustion engine, with two pistons moving against each other in each cylinder. In this type of engine, a compression space is created between two pistons in the middle of the cylinder.
Three-shaft motor
A three-shaft engine is a multi-shaft engine with crankshafts spaced apart in the three corners of a regular formation. According to the arrangement of the cylinders, we divide the three-shaft engine into:
Y Engine
A Y engine is a three-cylinder or three-row, three-shaft, three-piston internal combustion engine with counter-rotating pistons. This engine type has cylinders or rows of cylinders (if it is more than a three-cylinder engine) arranged around a common compression space. If it is a three-cylinder engine, it is also a flat engine.
Delta engine
A triangular engine is a three-cylinder or three-row, three-shaft two-piston combustion engine with counter-rotating pistons. With this type of engine, its cross-section forms the shape of a triangle, on the vertices of which the crankshafts are placed, and the cylinders, in turn, form the sides of the triangle.
There are two pistons in each cylinder. If it is a three-cylinder triangular engine, it is also a flat engine.
Four-shaft motor
A four-shaft engine has crankshafts spaced apart at the four corners of a quadrilateral. It is precisely from the design of this engine that its name is derived, namely a quadrilateral engine.
Square motor
A square engine is a four-cylinder or four-row, four-shaft, two-piston combustion engine with counter-rotating pistons. With this type of engine, its cross-section forms a quadrilateral shape. Crankshafts are placed on the vertices of the quadrangle, and the sides of the quadrangle, in turn, form cylinders.
Compression Ratio: What effect does it have on the engine?
Two pistons in each cylinder move against each other. The compression space is created between the two pistons in the middle of the cylinder. If a quadrilateral engine is only a four-cylinder, it is also included in the group of flat engines.
If you want to learn more about one of these engines, don't despair. In other articles, we will write about all the types of engines mentioned today in more detail.